Introduction
A brain stroke, also known simply as a stroke, is a critical medical emergency that can strike individuals of any age. It ranks as the fourth primary cause of mortality in the United States and is the most common cause of death among adults aged 45 to 64. Despite its potentially devastating consequences, early detection and prompt treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Recognizing the warning signs of a stroke is crucial for timely intervention. Common indicators include sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body. Other symptoms may include difficulty speaking or understanding speech, severe headaches without apparent cause, and impaired vision in one or both eyes.
Understanding these warning signs can empower individuals to act swiftly and seek medical assistance if they suspect someone may be experiencing a stroke episode. By proactively identifying risk factors such as high blood pressure, obesity, and smoking, lifestyle changes can be made to reduce the likelihood of suffering from a stroke. Promptly addressing stroke symptoms and implementing preventive measures can potentially save lives and minimize long-term disabilities associated with this severe condition.
A brain stroke is a critical medical emergency that arises when the flow of blood to the brain is interrupted. This interruption triggers a rapid deterioration of brain cells, with irreversible damage occurring within minutes. Symptoms of a stroke include sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, along with confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding speech. These warning signs necessitate immediate medical attention to prevent long-term disability or death.
There are two main types of strokes: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes result from blocked blood vessels in the brain, often due to blood clots. On the other hand, hemorrhagic strokes occur when weakened blood vessels rupture within the brain. Prompt treatment through clot-busting drugs and surgical intervention can mitigate the effects of a stroke if administered quickly enough.
Risk factors for experiencing a stroke include high blood pressure, smoking, obesity, and diabetes. Additionally, certain preexisting conditions, such as atrial fibrillation (an irregular heart rhythm), can heighten an individual’s susceptibility to suffering a stroke. Early recognition of symptoms and effective interventions are crucial in mitigating the long-term consequences of a brain stroke.
In this post, we are going to discuss the symptoms of a brain stroke, the causes of a brain stroke, and the various available treatments. We will also discuss the different cures for a brain stroke and how you can protect yourself from this serious medical condition. So whether you are a stroke survivor or a loved one of a stroke victim, read on to learn everything you need to know about this dangerous condition.
What are brain stroke symptoms?
Brain stroke is a severe medical condition that can result in several different symptoms depending on the part of the brain that is affected. Here are some of the most common ones: 1. Slurred speech 2. Changes in consciousness 3. Difficulty speaking or understanding 4. Inability to think clearly 5. Uncontrollable movements 6. Focal weakness 7. Difficulty walking 8. Inability to control facial muscles 9. Seizures 10. Loss of bladder or bowel control Some risk factors Brain stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident, can occur due to a variety of factors. While the specific causes may not always be clear, certain risk factors have been identified. These include advanced age, a family history of stroke, high blood pressure, and obesity. Additionally, smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol levels are also associated with an increased risk of experiencing a brain stroke. It is important to note that there is no single cure for brain stroke. However, various treatment options are available to help manage the condition and improve symptoms. Medications such as blood thinners and clot-busting drugs are often used in the acute phase of a stroke to prevent further damage. In some cases, surgery may also be recommended to address specific underlying issues that contributed to the stroke. Rehabilitation programs, including physical therapy and speech therapy, can aid in recovery and help individuals regain lost functions. Lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing chronic conditions can also play a pivotal role in preventing future strokes. Overall, early recognition of potential risk factors and prompt medical intervention are crucial in mitigating the impact of brain stroke on an individual’s health and well-being. If you or a loved one experiences any of these symptoms, getting medical help as soon as possible is essential. Many treatments are available; the sooner you get help, the better the chances of a successful outcome.What are the causes of brain stroke?
Brain strokes, also called cerebrovascular accidents, are a critical medical emergency with profound impacts on patients and their loved ones. A brain stroke disrupts blood flow to the brain, depriving brain cells of oxygen and essential nutrients. This can result in irreversible damage to the brain and its functions. The brain regulates our thoughts, emotions, and bodily processes. Therefore, any impairment to its function can devastate an individual’s quality of life.
Common symptoms of a brain stroke include sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm or leg, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, severe headache without known cause, and loss of balance or coordination. Most strokes are caused by a blockage preventing blood flow to the brain (ischemic stroke) or by a burst blood vessel causing bleeding in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke). Prompt medical treatment is crucial to minimize long-term disabilities and increase the chances of recovery from a stroke.
Brain stroke can occur in two main ways: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes are typically caused by a blood clot forming in an artery leading to the brain, often due to atherosclerosis – the buildup of fatty deposits known as plaques in the blood vessels. On the other hand, hemorrhagic strokes happen when a blood vessel ruptures, leading to bleeding in or around the brain.
Ischemic strokes account for about 80% of all strokes and are commonly associated with risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, smoking, and diabetes. When a clot blocks an artery in the brain, it disrupts the flow of oxygen-rich blood, leading to damage and cell death.
Hemorrhagic strokes, while less common than ischemic strokes, are often linked to conditions such as uncontrolled high blood pressure, aneurysms (weak areas in blood vessel walls), or arteriovenous malformations (abnormal tangles of blood vessels). The sudden bleeding puts pressure on surrounding brain tissue and can cause further complications.
Understanding the different causes and types of brain stroke is crucial for recognizing symptoms early and seeking immediate medical attention. Prompt treatment plays a significant role in minimizing long-term disability and improving outcomes for stroke survivors.
Various risk factors, such as age and gender, can influence brain strokes.
As individuals age, the risk of experiencing a stroke increases, particularly after the age of 55. Research has shown that men are more likely to have a stroke compared to women, though the reasons for this difference are still being explored. Additionally, lifestyle choices like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and physical inactivity can also raise the risk of having a stroke. Furthermore, certain medical conditions, including high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol levels, can contribute to an increased likelihood of experiencing a stroke. Identifying and managing these risk factors is crucial in preventing strokes and maintaining overall brain health.

Certain medical conditions, including high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease, and atrial fibrillation (an irregular heartbeat), are known to increase the risk of brain stroke. These conditions can disrupt the normal functioning of blood vessels and increase the likelihood of a blockage or rupture in the brain’s blood supply.
In addition to medical conditions, lifestyle factors also play a crucial role in the development of brain stroke. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity are all significant contributors to an individual’s susceptibility to stroke.
Smoking, for instance, damages blood vessels and increases the buildup of fatty deposits in arteries. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to high blood pressure and irregular heart rhythms, which may raise the risk of brain stroke.
When combined with other risk factors such as medical conditions or genetics, these lifestyle factors can significantly elevate an individual’s likelihood of experiencing a debilitating brain stroke.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by quitting smoking, moderating alcohol intake, exercising regularly, and following a balanced diet is crucial in minimizing the risk of brain stroke. Regular health check-ups can help identify any underlying medical conditions predisposing an individual to this life-threatening condition.
It is essential to understand that specific causes and risk factors can elevate the chances of a brain stroke, but having these factors does not automatically mean a stroke will happen. However, being aware of these factors and taking proactive measures through lifestyle modifications and medical intervention can markedly lower the risk and support brain health.
Common causes and risk factors for strokes include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and excessive alcohol consumption. These factors can lead to the development of plaque in the arteries or cause blood clots, which are vital contributors to strokes. Additionally, age, family history of strokes, and certain genetic conditions can also increase an individual’s susceptibility to experiencing a stroke.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet low in saturated fats and salt, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress levels, and avoiding tobacco use can significantly reduce the risk of stroke. Furthermore, staying proactive about monitoring and managing existing health conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes is crucial in minimizing the likelihood of having a stroke.
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers for preventive care are vital in identifying potential risk factors early on and developing an effective prevention plan. It’s essential to prioritize overall brain health by understanding these risks and taking steps to mitigate them.
How can brain stroke be prevented?
Brain stroke is a severe condition that can cause significant damage to the brain. It is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States and the leading cause of severe long-term disability. Preventing brain stroke is crucial, and there are several strategies to help reduce the risk of this debilitating condition. Firstly, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the signs and symptoms of a brain stroke, such as sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, particularly on one side of the body, confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech, and severe headache. Secondly, prompt medical attention is critical if you experience these symptoms. Seeking immediate help can significantly improve the chances of recovery and minimize potential long-term effects. In addition to being symptom-aware, maintaining an active lifestyle and adopting healthy habits is critical to reducing the risk of brain stroke. Engaging in regular physical activity and eating a balanced diet can help control factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and obesity, which contribute to the development of strokes. Furthermore, avoiding smoking is crucial in stroke prevention since smoking increases the likelihood of blood clots forming in the arteries leading to the brain. By implementing these simple yet effective tips into your daily routine, you can take proactive steps towards preventing brain stroke and promoting overall health and well-being.Some measures to enhance recovery
There are many possible cures for brain stroke, and it’s essential to seek medical help as soon as possible. However, some things you can do to help improve your chances of a successful recovery include:
> Seek medical help as quickly as possible.
> Keep active and movable as much as possible.
> Drink plenty of fluids.
> Elevate your head and neck as much as possible.
> Take medications as prescribed by a doctor.
> Keep a positive outlook.
> Communicate with your loved ones.
> Seek religious or spiritual guidance.
> Seek professional help.
> Stay positive.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle and effectively managing risk factors, you can significantly reduce your chances of experiencing a brain stroke. Prevention is vital, and taking proactive steps towards your health today can lead to a healthier future.
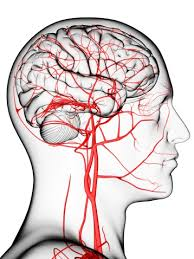



3 thoughts on “<strong>Brain stroke symptoms, causes and cures</strong>”